- Recommended name
- Gymnodimine A
- Synonyms
- Gymnodimine-A
- Recommended acronym
- GYM-A
- Abbreviation
Progenitors
- Name
- Karenia selliformis
- Note
- Seki et al., 1995 Haywood et al., 2004
- Name
- Alexandrium ostenfeldii
- Note
- Martens et al., 2017
Vector Species
- Name
- Ostrea chilensis
- Note
- Oysters (Tiostrea chilensis = Ostrea chilensis) MacKenzie et al., 1996 Stirling, 2001
- Name
- Perna canaliculus
- Note
- Stirling, 2001
- Name
- Pecten novaezelandiae
- Note
- Stirling, 2001
- Name
- Paphies australis
- Note
- Stirling, 2001
- Name
- Haliotis iris
- Note
- Stirling, 2001
- Name
- Mytilus galloprovincialis
- Note
- Stirling, 2001 Lamas et al., 2021
- Name
- Choromytilus meridionalis
- Note
- Krock et al., 2009
- Name
- Magallana hongkongensis
- Note
- Ji et al., 2022
- Name
- Pinctada imbricata
- Note
- Ji et al., 2022
- Name
- Antigona lamellaris
- Note
- Ji et al., 2022
- Name
- Marcia hiantina
- Note
- Ji et al., 2022
- Name
- Tegillarca granosa
- Note
- Ji et al., 2022
- Name
- Perna viridis
- Note
- Ji et al., 2022
- Name
- Ruditapes philippinarum
- Note
- Geng et al., 2022
- Name
- Anadara kagoshimensis
- Note
- Geng et al., 2022
- Name
- Dendrophysa russelii
- Note
- Li et al., 2021
- Name
- Evynnis cardinalis
- Note
- Li et al., 2021
- Name
- Johnius heterolepis
- Note
- Li et al., 2021
- Name
- Priacanthus macracanthus
- Note
- Li et al., 2021
- Name
- Trypauchen vagina
- Note
- Li et al., 2021
- Name
- Harpiosquilla harpax
- Note
- Li et al., 2021
- Name
- Metapenaeus affinis
- Note
- Li et al., 2021
- Name
- Metapenaeus ensis
- Note
- Li et al., 2021
- Name
- Portunus sanguinolentus
- Note
- Li et al., 2021
- Name
- Portunus trituberculatus
- Note
- Li et al., 2021
- Name
- Anadara ferruginea
- Note
- Li et al., 2021
- Name
- Bufonaria rana
- Note
- Li et al., 2021
- Name
- Fulvia australis
- Note
- Li et al., 2021
- Name
- Murex trapa
- Note
- Li et al., 2021
- Name
- Nassarius siquijorensis
- Note
- Li et al., 2021
- Name
- Turritella bacillum
- Note
- Li et al., 2021
- Name
- Magallana gigas
- Note
- Magallana gigas=Crassostrea gigas O'Neill et al., 2021
- Name
- Ruditapes decussatus
- Note
- De la Iglesia et al., 2013
References
- Tetsuya Seki, 1995
- Seki, T., Satake, M., Mackenzie, L., Kaspar, H. F., & Yasumoto, T. (1995). Gymnodimine, a new marine toxin of unprecedented structure isolated from New Zealand oysters and the dinoflagellate, Gymnodinium sp. Tetrahedron letters, 36(39), 7093-7096.
- Allison J. Haywood, 2004
- Haywood, A. J., Steidinger, K. A., Truby, E. W., Bergquist, P. R., Bergquist, P. L., Adamson, J., & Mackenzie, L. (2004). Comparative morphology and molecular phylogenetic analysis of three new species of the genus Karenia (Dinophyceae) from New Zealand 1. Journal of Phycology, 40(1), 165-179.
- Helge Martens, 2017
- Martens, H., Tillmann, U., Harju, K., Dell’Aversano, C., Tartaglione, L., & Krock, B. (2017). Toxin variability estimations of 68 Alexandrium ostenfeldii (Dinophyceae) strains from The Netherlands reveal a novel abundant gymnodimine. Microorganisms, 5(2), 29.
- David J. Stirling, 2001
- Stirling, D. J. (2001). Survey of historical New Zealand shellfish samples for accumulation of gymnodimine. New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research, 35(4), 851-857.
- Bernd Krock, 2009
- Krock, B., Pitcher, G. C., Ntuli, J., & Cembella, A. D. (2009). Confirmed identification of gymnodimine in oysters from the west coast of South Africa by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. African Journal of Marine Science, 31(1), 113-118.
- Ying Ji, 2022
- Ji, Y., Yan, G., Wang, G., Liu, J., Tang, Z., Yan, Y., ... & Li, A. (2022). Prevalence and distribution of domoic acid and cyclic imines in bivalve mollusks from Beibu Gulf, China. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 423, 127078.
- Huixia Geng, 2022
- Geng, H., Sun, H., Liu, C., Kong, F., Zhang, Q., Yan, T., & Yu, R. (2022). Screening for lipophilic marine toxins and their potential producers in coastal waters of Weihai in autumn, 2020. Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 40(6), 2218-2230.
- Jing Li, 2021
- Li, J., Ruan, Y., Mak, Y. L., Zhang, X., Lam, J. C., Leung, K. M., & Lam, P. K. (2021). Occurrence and trophodynamics of marine lipophilic phycotoxins in a subtropical marine food web. Environmental Science & Technology, 55(13), 8829-8838.
- J.Pablo Lamas, 2021
- Lamas, J. P., Arévalo, F., Moroño, Á., Correa, J., Rossignoli, A. E., & Blanco, J. (2021). Gymnodimine A in mollusks from the north Atlantic Coast of Spain: Prevalence, concentration, and relationship with spirolides. Environmental Pollution, 279, 116919.
- Simone Bacchiocchi, 2020
- Bacchiocchi, S., Siracusa, M., Campacci, D., Ciriaci, M., Dubbini, A., Tavoloni, T., ... & Piersanti, A. (2020). Cyclic Imines (CIs) in Mussels from North-Central Adriatic Sea: First Evidence of Gymnodimine A in Italy. Toxins, 12(6), 370.
- Alison O'Neill, 2021
- O'Neill, A., Morrell, N., Turner, A. D., & Maskrey, B. H. (2021). Method performance verification for the combined detection and quantitation of the marine neurotoxins cyclic imines and brevetoxin shellfish metabolites in mussels (Mytilus edulis) and oysters (Crassostrea gigas) by UHPLC-MS/MS. Journal of Chromatography B, 1179, 122864.
- De la Iglesia, P., 2013
- De la Iglesia, P., McCarron, P., Diogène, J., & Quilliam, M. A. (2013). Discovery of gymnodimine fatty acid ester metabolites in shellfish using liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 27(5), 643-653.
- Structure
-
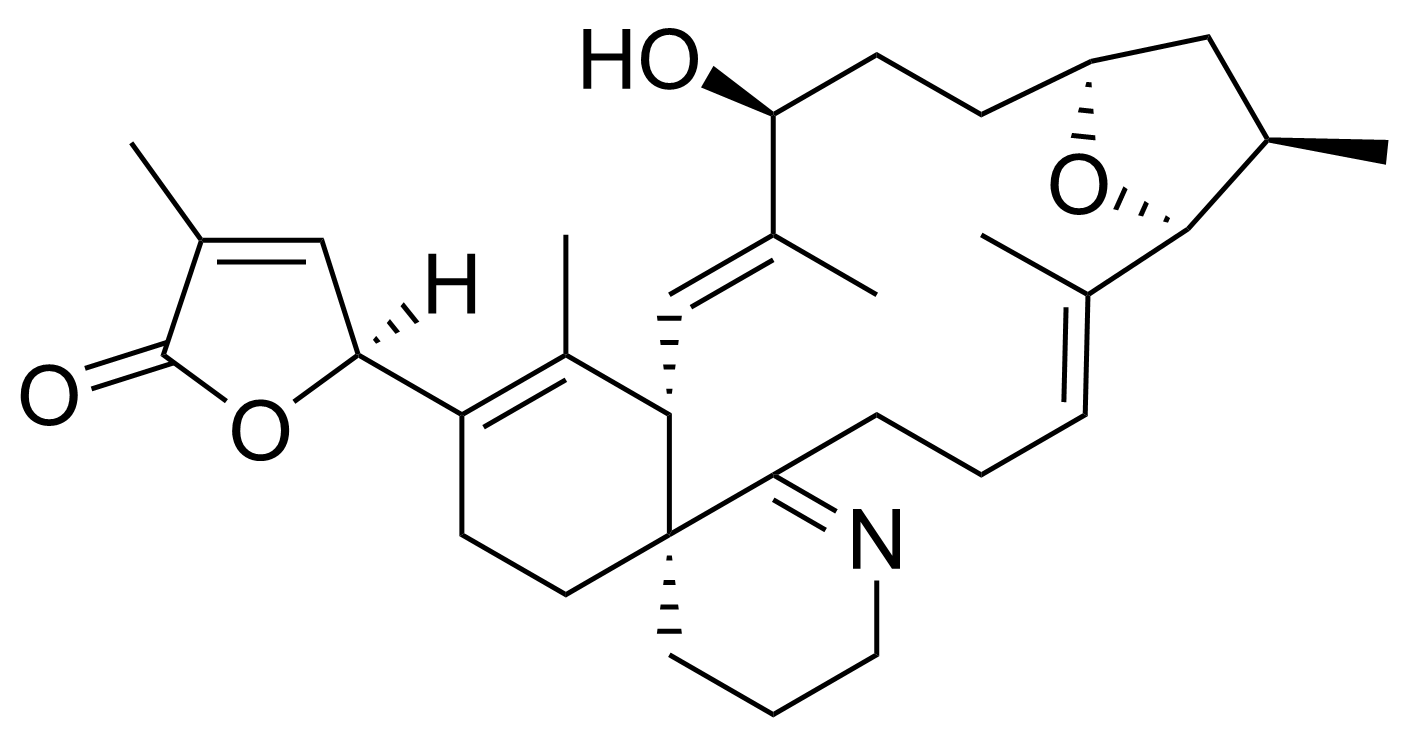
- Formula
- C32H45NO4
- Exact mono-isotopic mass
- 507.33486
- Molfile
- n/a
- Alternative molfiles
- n/a
- SMILES
- CC1=C([C@]2([H])C=C(C)C(O2)=O)CC[C@@]3(CCCN=C3CC/C=C4C)[C@H]1/C=C(C)/[C@H](CC[C@@H]5O[C@H]\4[C@H](C)C5)O
- Alternative SMILES
- C[C@@H]1C[C@H]2CC[C@@H](/C(=C/[C@H]3C(=C(CC[C@@]34CCCN=C4CC/C=C(/[C@@H]1O2)\C)[C@@H]5C=C(C(=O)O5)C)C)/C)O
- InChi key
- DVXZVCNEGRKLMW-KQZYCKQJSA-N
- Alternative InChi keys
- n/a
- InChi
- InChI=1S/C32H45NO4/c1-19-8-6-9-29-32(13-7-15-33-29)14-12-25(28-18-22(4)31(35)37-28)23(5)26(32)17-20(2)27(34)11-10-24-16-21(3)30(19)36-24/h8,17-18,21,24,26-28,30,34H,6-7,9-16H2,1-5H3/b19-8+,20-17+/t21-,24+,26+,27+,28+,30-,32+/m1/s1
- Alternative InChis
- Spectra available
- True
- Chem files
References
- Michael Stewart, 1997
- Stewart, M., Blunt, J. W., Munro, M. H., Robinson, W. T., & Hannah, D. J. (1997). The absolute stereochemistry of the New Zealand shellfish toxin gymnodimine. Tetrahedron Letters, 38(27), 4889-4890.
- Certified
- True
- Certified links
-
- National Research Council Canada
CRM-GYM-b Gymnodimine Calibration Solution CRM (0.5 mL /ampoule)
- National Research Council Canada
- Non certified reference material
- True
Chemical analysis
- Research
- True
- Standardized
- Unknown
- Validated
- Unknown
- Official
- n/a
Structure recognition assays
- Research
- Unknown
- Standardized
- Unknown
- Validated
- Unknown
- Official
- n/a
Functional assays
- Research
- True
- Standardized
- Unknown
- Validated
- Unknown
- Official
- n/a
Animal assays
- Research
- True
- Standardized
- Unknown
- Validated
- Unknown
- Official
- n/a
References
- Takeshi YASUMOTO, 1978
- Mouse Bioassay Yasumoto, T., Oshima, Y., and Yamaguchi, M., 1978. Occurrence of a new type of shellfish poisoning in Tohoku district. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Sci. Fish. 44: 1249–1255.
- OECD, 2001
- Mouse Bioassay OECD, 2001. OECD Guideline for Testing of Chemicals 425. Acute Oral Toxicity—Up and Down Procedure. Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, Paris, France (http://www.epa. gov/oppfead1/harmonization/docs/E425guideline.pdf)
- Lincoln MacKenzie, 2002
- LC-MS/MS MacKenzie, L., Holland, P., McNabb, P., Beuzenberg, V., Selwood, A., & Suzuki, T. (2002). Complex toxin profiles in phytoplankton and Greenshell mussels (Perna canaliculus), revealed by LC–MS/MS analysis. Toxicon, 40(9), 1321-1330.
- Paul McNabb, 2005
- LC-MS/MS McNabb, P., Selwood, A. I., Holland, P. T., & Collaborators: Aasen J., Aune T., Eaglesham G., Hess P., Igarishi M., Quilliam M., Slattery D., Van de Riet J., Van Egmond H., Van den Top H., Yasumoto T. (2005). Multiresidue method for determination of algal toxins in shellfish: Single-laboratory validation and interlaboratory study. Journal of AOAC International, 88(3), 761-772.
- Jiangbing Qiu, 2020
- LC-MS/MS Qiu, J., Chen, H., Ji, Y., Li, T., & Li, A. (2020). Evaluation of different strategies to minimize the matrix effects on LC-MS/MS analysis of multiple lipophilic shellfish toxins in both acidic and alkaline chromatographic conditions. Toxicon, 188, 16-26.
- Elie Fux, 2007
- UPLC-MS/MS Fux, E., McMillan, D., Bire, R., & Hess, P. (2007). Development of an ultra-performance liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry method for the detection of lipophilic marine toxins. Journal of chromatography A, 1157(1-2), 273-280.
- Laura P. Rodríguez, 2011
- Functional Assays Rodriguez, L. P., Vilarino, N., Molgó, J., Aráoz, R., Antelo, A., Vieytes, M. R., & Botana, L. M. (2011). Solid-phase receptor-based assay for the detection of cyclic imines by chemiluminescence, fluorescence, or colorimetry. Analytical chemistry, 83(15), 5857-5863.
- Natalia Vilariño, 2009
- Functional Assays Vilarino, N., Fonfria, E. S., Molgo, J., Araoz, R., & Botana, L. M. (2009). Detection of gymnodimine-A and 13-desmethyl C spirolide phycotoxins by fluorescence polarization. Analytical chemistry, 81(7), 2708-2714.
- RETURN TO ISSUEPREVARTICLENEXT Coupling the Torpedo Microplate-Receptor Binding Assay with Mass Spectrometry to Detect Cyclic Imine Neurotoxins Rómulo Aráoz, 2012
- Functional Assays Aráoz, R., Ramos, S., Pelissier, F., Guérineau, V., Benoit, E., Vilariño, N., ... & Molgó, J. (2012). Coupling the Torpedo microplate-receptor binding assay with mass spectrometry to detect cyclic imine neurotoxins. Analytical chemistry, 84(23), 10445-10453.
- Regulatory status
- False
- Human toxic syndrome(s)
- n/a
- Organ system toxicity
- Neurotoxicity
- Risk assessment
- Unknown
- Molecular targets known
- True
- Molecular targets
- Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors
- Toxic to aquatic animals
- Unknown
- TEF available
- Unknown
Risk assessment References
- Rex Munday, 2006
- Munday, R. (2006). Toxicological requirements for risk assessment of shellfish contaminants: a review. African Journal of Marine Science, 28(2), 447-449.
- Rex Munday, 2004
- Munday, R., Towers, N. R., Mackenzie, L., Beuzenberg, V., Holland, P. T., & Miles, C. O. (2004). Acute toxicity of gymnodimine to mice. Toxicon, 44(2), 173-178.
- Notes